Climate change has become a serious threat to agriculture. Extreme weather events and changes in weather patterns have been increasingly disrupting the equilibrium on which farming practices have been built, destroying crops. On the other hand, agribusiness technology, data traceability, and farming advancements are leading a revolution to not only overcome the obstacles created by climate change but also as tools to create a more nature-positive food system, that meets the world’s nutritional needs, while respecting nature’s fragile balance.
Temperature Changes
In agricultural fields, temperature changes can have an unpredictable influence. Rising global temperatures bring heatwaves that can set ablaze the crops, diminishing their yields. Conversely, unexpected frosts arrive often without warning, wreaking havoc on farms.
Agribusiness technology has been a massive help in monitoring the weather forecast and also making careful use of the available resources. Precision agriculture, guided by the meticulous insights derived from advanced sensors and satellites, empowers farmers to monitor temperature fluctuations in real-time, such as Soiltech Wireless, Chrysa Labs, and Precision AI. In the controlled environment of greenhouses and vertical farms, farmers have mastered precise temperature regulation, guarding crops against the whims of the weather.
Changing Rainfall Patterns
Climate change causes unpredictable precipitations. The fields often suffer from erratic rainfall patterns. Prolonged droughts test the endurance of crops, while floods challenge our planting and harvest schedules.
In the age of data traceability, we have unlocked the knowledge regarding precipitation trends. Armed with advanced weather forecasting models and satellite imagery, farmers make decisions rooted in foresight, adapting to the unforeseeable patterns of the weather. Rainwater harvesting and drip irrigation systems emerge as eco-friendly solutions, conserving our precious water resources.
Water Scarcity
Water scarcity grows more formidable with each passing season. The wasteful use of water resources strains aquifers and depletes underground reserves and farming advancements rise to meet this challenge.
Precision irrigation systems, fine-tuned by data-driven strategies, can support farmers in optimizing water usage. Dryland farming and soil moisture monitoring techniques, it can maximize water efficiency while preserving our environment. According to NETAFIM "Agriculture consumes 70 percent of the global freshwater. And yet, in many places around the world, water is wasted through inefficient traditional irrigation methods" showcasing the importance of technology in such a situation.
Shifts in Growing Zones
Climate change is redefining the familiar growing zones, pushing farmers and gardeners to adapt. Traditional crops find themselves ill-suited to changing conditions, creating the need of a radical shift in our agricultural landscapes. As growing zones become warmer, farmers in the US for example, will have to adjust the type of crops they grow, choosing more adaptable varieties that are compatible with wider and warmer ranges of temperatures.
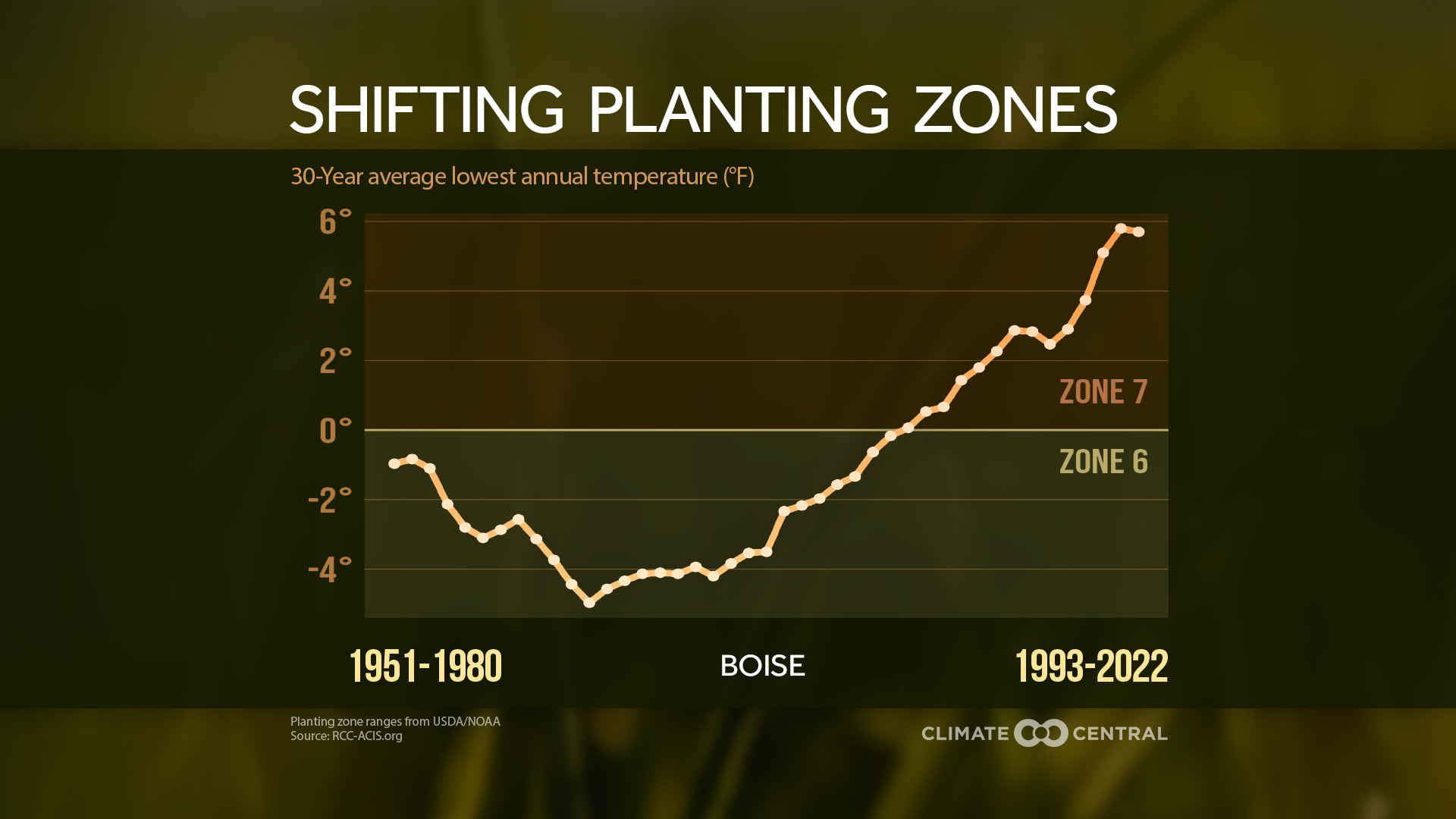
Agribusiness technology emerges as a possible solution. Data analytics and predictive modeling become a solution for resilient cultivation. The science of genetics, bolstered by selective breeding and genetic modification, created heat-tolerant and drought-resistant crop varieties, enabling us to sow stronger seeds in previously inhospitable terrain.
Loss of Biodiversity
Amidst the evolving problem of climate change, biodiversity faces a complicated journey. Pollinators like bees are struggling in the face of changing temperatures, diminishing our crop yields through inadequate pollination.
As accessible data become increasingly available, so does our capacity to analyze it, if we collect and analyze it meaningfully, these insights can help us understand nature’s needs better. By meticulously monitoring ecosystems and tracking pollinator populations, farmers can assume the role of guardians, nurturing biodiversity back to health. Crop rotation become crucial for our sustainable agriculture, ensuring the vitality of our ecosystems.
Economic Impact
The economic repercussions of climate change on agriculture reverberate through the markets and the fields. Crop failures, loss in the soil’s fertility, and soaring input costs cast a shadow of financial uncertainty over farming communities. In addition, estimates show that in the last 40 years, floods have caused around €250 billion in losses.
Yet, amidst these challenges, agribusiness technology and data traceability emerge as the pillars of economic change in the industry. Real-time market data and supply chain transparency empower farmers to make informed choices, adapt to market fluctuations, and secure fair compensation for their work. Traceability systems shine a light on the path of sustainability, enticing consumers to choose responsibly grown products and fortifying our industry's future.
As we can see, AgTech innovations are supporting farmers in optimizing their land’s resources and in collecting useful data that can inform and help build accurate strategies. However, farmers cannot invest and drive these changes alone. The whole food system from producer to consumers has a role to play in supporting this process towards increasingly sustainable practices.
For this reason, it is also important to strengthen transparency and information flow around farming activities, in order to actively those farmers and initiatives that are championing sustainably driven innovations and farming practices.
What is SoilHive?
Discover more about our other service SoilHive and how it can revolutionize collaboration in the Food & Ag industry and enhance soil data accessibility. Explore more at:




